Project-raspberry-pi-router-dhcp-nat-access-point-dns-block-ads-vpn.md
Please note:
This post is still in "WORK IN PROGRESS" mode..
USE AT YOUR OWN RESPONSABILITY
diskutil list
(...)
/dev/disk4 (external, physical): <<<<------- THAT IS MY EXTERNAL MICRO-SD CARD
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: FDisk_partition_scheme *31.9 GB disk4
1: Windows_FAT_32 boot 46.0 MB disk4s1
2: Linux 31.9 GB disk4s2
````
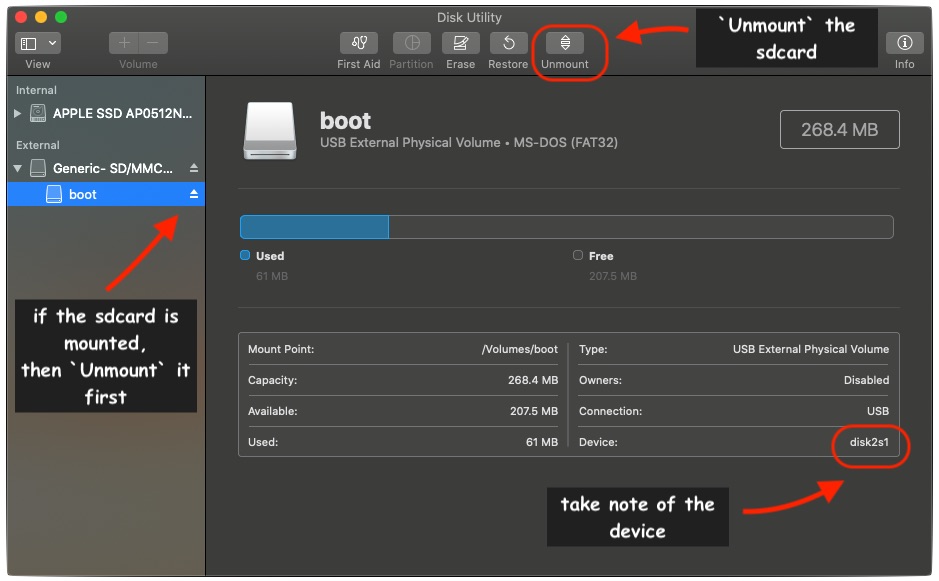
Unmount the disk
```bash
diskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk4
Unmount of all volumes on disk4 was successful
After extracting the image file from the Raspberry Pi OS zip file,
copy it using dd command into the SD-card disk.
Note the /dev/rdisk4/, rdisk is the "raw disk", this speeds up the copying.
You can check my other post about micro-sd writing speed test in here https://antonio.cloud/linux/raspberry-pi/micro-sd-card-write-speed-test/.
sudo dd bs=1m if=2021-05-07-raspios-buster-armhf-lite.img of=/dev/rdisk4; sync
1788+0 records in
1788+0 records out
1874853888 bytes transferred in 27.184011 secs (68968994 bytes/sec)
While I have the micro-sd card in the laptop, I want the Raspberry Pi to have SSH Server enabled and conncet to a wifi (wireless) network.
Remeber to update for your settings, update for your wifi name, password and country.
In priority, then highest wins.
touch /Volumes/boot/ssh
touch /Volumes/boot/wpa_supplicant.conf
#vim /Volumes/boot/wpa_supplicant.conf
cat <<EOF > /Volumes/boot/wpa_supplicant.conf
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
country=GB
network={
scan_ssid=1
priority=5
ssid="MY_WIFI_NAME"
psk="MY_WIFI_PASSWORD"
proto=RSN
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
pairwise=CCMP
auth_alg=OPEN
}
network={
scan_ssid=1
priority=0
ssid="MY_OTHER_WIFI_NAME"
psk="MY_OTHER_WIFI_PASSWORD"
proto=RSN
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
pairwise=CCMP
auth_alg=OPEN
}
EOF
While in here, you can disable IPv6 for the Raspberry Pi.
add ipv6.disable=1 at the almost end of the file cmdline.txt , add it just before the ini=/.... script that will run on first boot.
vim /Volumes/boot/cmdline.txt
console=serial0,115200 console=tty1 root=PARTUUID=xxxxaxxxa-xx rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait quiet ipv6.disable=1 init=/usr/lib/raspi-config/init_resize.sh
and to disable Bluetooth, add the below to the end of config.txt file
vim /Volumes/boot/config.txt
# Disable Bluetooth
dtoverlay=disable-bt
Then eject the "disk", the micro-sd card
diskutil eject /dev/disk4
Disk /dev/disk4 ejected
Insert the micro-sd card in the Raspberry Pi, turn the Raspberry Pi on and "look" for it on your router or look for a new device on your wifi (wireless) network.
Them, SSH into the Raspberry Pi and let the fun stuff (configurations) beggin!
I my case, I used nmap to find the new device on the network.
nmap -sT -p 22 --open 192.168.1.0/24
when you find your new device
ssh [email protected] <<--- IP of the new device, Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi default password if raspberry
1) As soon as you connect to the Raspberry Pi, change the default with sudo passwd pi command
sudo passwd pi
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
2) Make sure your Raspberry Pi is up-to-date
sudo apt-get update
(...)
sudo apt-get upgrade
(...)
or shorter version if some extras
sudo su
#set +x
apt clean
apt update -y
apt full-upgrade -y
apt autoremove -y
apt install vim -y
add your favourite alias is you have some
echo "alias ll='ls -alhF --group-directories-first --color=always'" >> /etc/bash.bashrc
```
Reboot and reconnect
3) Update the Raspberry Pi firmware (optional)
Update the Raspberry Pi firmware is option
```bash
sudo rpi-update
4) Use own Raspberry Pi config command
Review configurations and change what is meanful for you.
I recommend to give a name to the Raspberry Pi to meaninful.
Reboot
(you can skip this steps if you did this on the "additional bonus step" mentioned above.)
https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?t=256349
Add ipv6.disable=1 to the end of /boot/cmdline.txt file
Reboot
If you don't need Bluetooth, you can disable it and remove unnecessary files
Edit the file /boot/config.txt and to the end the following
sudo vim /boot/config.txt
# Disable Bluetooth
dtoverlay=disable-bt
save and exit file
sudo systemctl disable hciuart.service
sudo systemctl disable bluealsa.service
sudo systemctl disable bluetooth.service
Reboot
Just physically connect the additional external USB
Important
This is not the same for all the devices.
You migh need to research the correct drivers for your specific device.
I followed these instructions - https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8812au>
sudo apt-get install raspberrypi-kernel-headers
sudo apt install make gcc git
sudo apt install dkms
git clone -b v5.6.4.2 https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8812au.git
cd rtl*
(....)
remaining instructions here - https://github.com/aircrack-ng/rtl8812au>
In this project I used the Raspberri Pi 4 onboard wireless as Access Point, device wlan0
for this, I used (and adopted to my setup) this guide https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/wireless/access-point-routed.md
sudo apt install hostapd
sudo systemctl unmask hostapd
sudo systemctl enable hostapd
sudo apt install dnsmasq
sudo apt install -y netfilter-persistent iptables-persistent
# sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt install -y netfilter-persistent iptables-persistent
Define the wireless interface IP configuration
sudo vim /etc/dhcpcd.conf
interface wlan0
static ip_address=192.168.4.1/24
nohook wpa_supplicant
ll /etc/wpa_supplicant/
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 937 Apr 16 14:07 action_wpa.sh*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 25K Apr 16 14:07 functions.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.6K Apr 16 14:07 ifupdown.sh*
-rw------- 1 root root 506 Aug 20 16:38 wpa_supplicant.conf
-rw------- 1 root root 496 Aug 20 16:37 wpa_supplicant-wlan0.conf
-rw------- 1 root root 477 Aug 20 16:35 wpa_supplicant-wlan1.conf
Raspberry Pi, randomly the onboard wireles device wlan0 becomed wlan1, below was a solution to keep the Raspberry Pi wlan0 and wlan1 persistent across reboots.
source and thank you to https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=198946
cat /etc/udev/rules.d/72-wlan-geo-dependent.rules
# source
# https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=198946
#
##
# +-----------------+
# | 1-1.1.2 | 1-1.3 |
# +------+ +---------+-------+
# | eth0 | | 1-1.1.3 | 1-1.2 |
# +------+ +-----------------+ (RPI USB ports with position dependent device names for up to 4 optional wifi dongles)
#
#
# | wlan0 | (onboard wifi)
#
ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", SUBSYSTEMS=="sdio", KERNELS=="mmc1:0001:1", NAME="wlan0"
ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", KERNELS=="1-1.1.2", NAME="wlan1"
ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", KERNELS=="1-1.1.3", NAME="wlan1"
ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", KERNELS=="1-1.3", NAME="wlan1"
ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", KERNELS=="1-1.2", NAME="wlan1"
# when using the lines below, only one WiFi device type can be used at a time
#ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", DRIVERS=="brcmfmac", NAME="wlan0"
#ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", DRIVERS=="rtl8192cu", NAME="wlan1"
sudo vim /etc/sysctl.d/routed-ap.conf
# https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/wireless/access-point-routed.md
# Enable IPv4 routing
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
"Mask" your Access point clients leaving your network.
Meaninig, mask the eth0 or wlan0 or whatever interface your Raspberry PI is connect to the internet side.
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o wlan1 -j MASQUERADE
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
sudo netfilter-persistent save
sudo cat /etc/iptables/rules.v4
Filtering rules are saved to the directory /etc/iptables/.
If in the future you change the configuration of your firewall, make sure to save the configuration before rebooting.
sudo mv /etc/dnsmasq.conf /etc/dnsmasq.conf.orig
sudo vim /etc/dnsmasq.conf
interface=wlan1
# Listening interface
dhcp-range=192.168.3.101,192.168.3.199,255.255.255.0,12h
# Pool of IP addresses served via DHCP
domain=wlan03
# Local wireless DNS domain
address=/gw.wlan03/192.168.3.1
# Alias for this router
To ensure WiFi radio is not blocked on your Raspberry Pi, execute the following command:
Create the hostapd configuration file, located at /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf,
to add the various parameters for your new wireless network.
sudo vim /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf
Add the information below to the configuration file.
country_code=GB
interface=wlan1
ssid=MYWIFI_AP_NAME
## for 2.4Ghz
#hw_mode=g
#channel=7
## for 5GHz
hw_mode=a
channel=36
macaddr_acl=0
auth_algs=1
ignore_broadcast_ssid=0
wpa=2
wpa_passphrase=MY_WIFI_AP_PASSWORD
wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
wpa_pairwise=TKIP
rsn_pairwise=CCMP
Note the line country_code=GB:
it configures the computer to use the correct wireless frequencies in the United Kingdom.
Adapt this line and specify the two-letter ISO code of your country. See Wikipedia for a list of two-letter ISO 3166-1 country codes.
To use the 5 GHz band, you can change the operations mode from hw_mode=g to hw_mode=a.
Possible values for hw_mode are:
a = IEEE 802.11a (5 GHz) (Raspberry Pi 3B+ onwards)
b = IEEE 802.11b (2.4 GHz)
g = IEEE 802.11g (2.4 GHz)
Note that when changing the hw_mode, you may need to also change the channel - see Wikipedia for a list of allowed combinations.
To avoid conflits with wlan0 and wlan1, I want the hostapd service to run only on the wlan0
cd /etc/hostapd/
sudo mv hostapd.conf wlan0.conf
systemctl | grep hostapd
sudo systemctl | grep wpa
sudo systemctl disable [email protected]
sudo systemctl status hostapd.service
sudo systemctl disable hostapd.service
sudo systemctl stop hostapd.service
## here enable hostapd just on interface wlan0
sudo systemctl enable [email protected]
ifconfig
sudo reboot
Now restart your Raspberry Pi and verify that the wireless access point becomes automatically available.
Once your Raspberry Pi has restarted, search for wireless networks with your wireless client.
The network SSID you specified in file /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf should now be present, and it should be accessible with the specified password.
https://raspberrypi.stackexchange.com/questions/37920/how-do-i-set-up-networking-wifi-static-ip-address-on-raspbian-raspberry-pi-os/37921#use-different-wpa_supplicant-files
wlan0 <--- Is the onboard wireless device to be as Wireless Access Point
wlan1 <--- Is the additional USB wireless device that connects to the local wireless for internet access
eth0 ← if connected to local network, will also provide internet for the wireless users connects to the wireless access point on wlan1
ls -alhF /etc/wpa_supplicant/
total 52K
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4.0K Aug 2 09:19 ./
drwxr-xr-x 82 root root 4.0K Aug 2 09:18 ../
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 937 Apr 16 14:07 action_wpa.sh*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 25K Apr 16 14:07 functions.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.6K Apr 16 14:07 ifupdown.sh*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 2 09:19 wpa_supplicant.conf <---- default wireless setup for all interfaces (I left this file empty)
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 237 Aug 2 09:19 wpa_supplicant-wlan1.conf <------ this is the interface that I want the Raspberry Pi to use to connect to the wireless internet.
WORK-IN-PROGRESS
next to do
Happy learning
Antonio Feijao UK